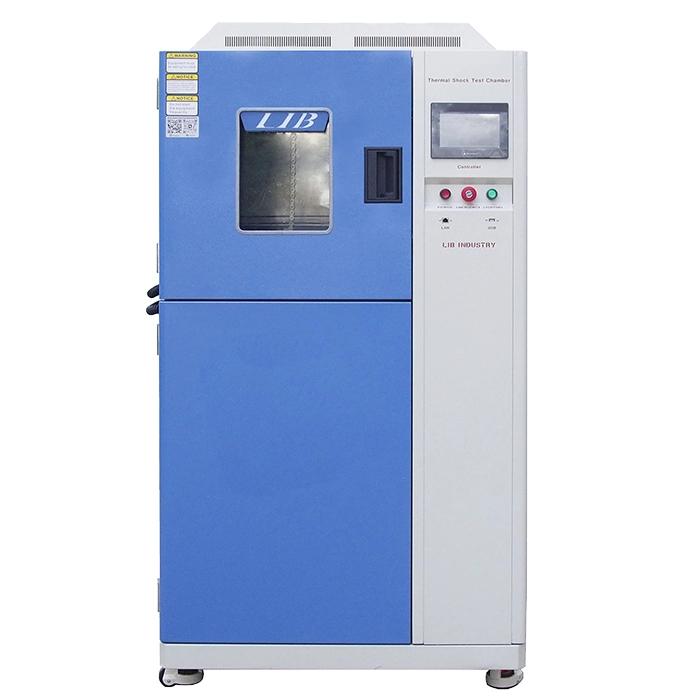
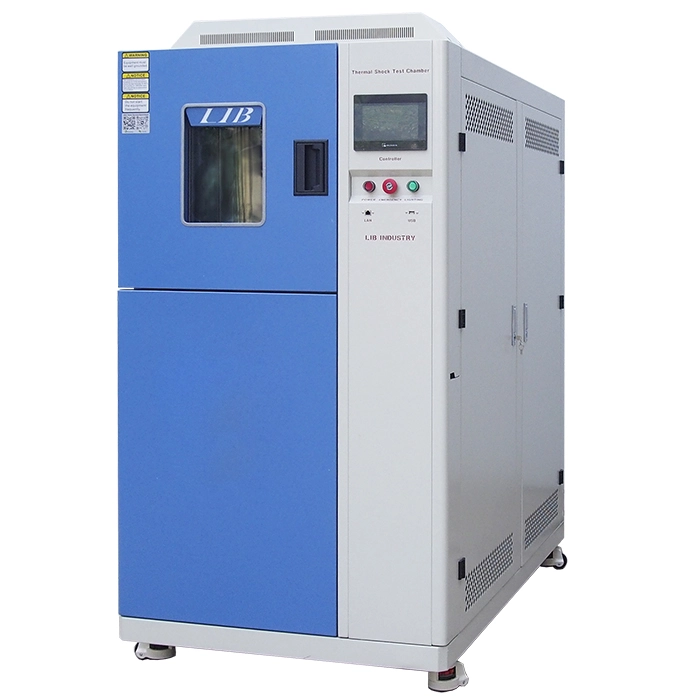
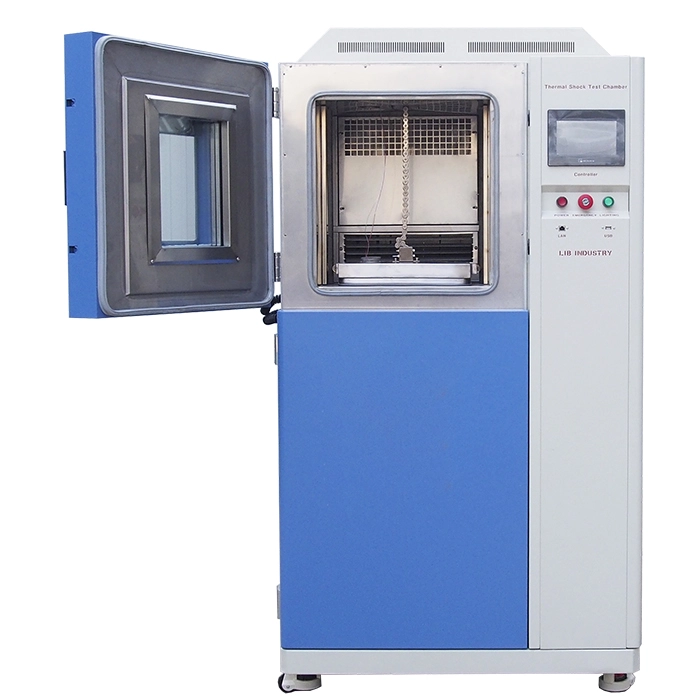
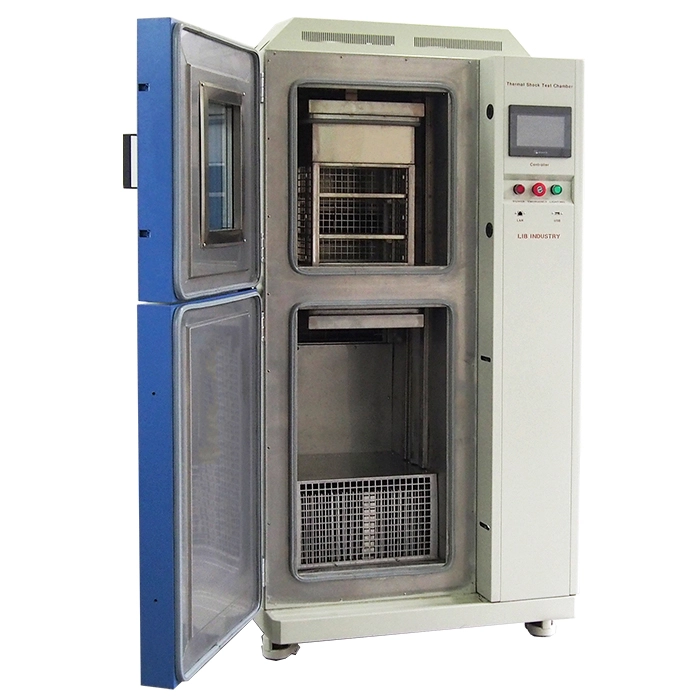
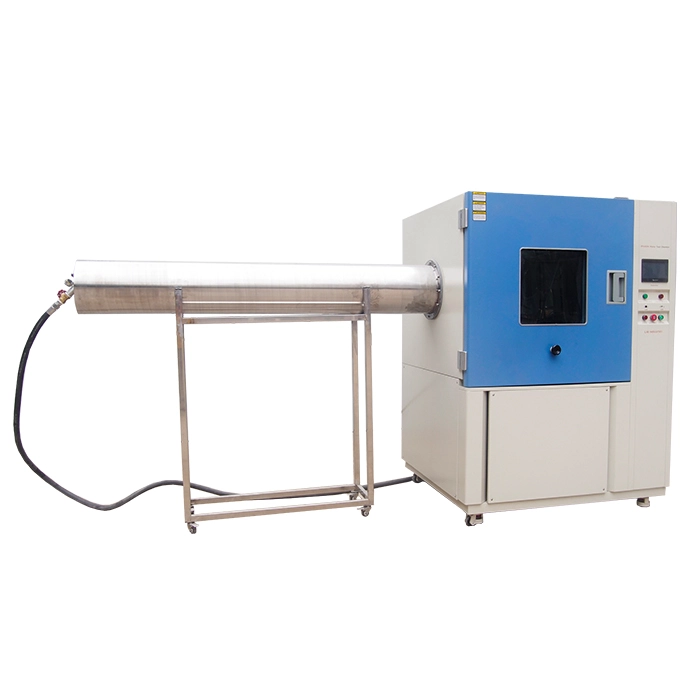
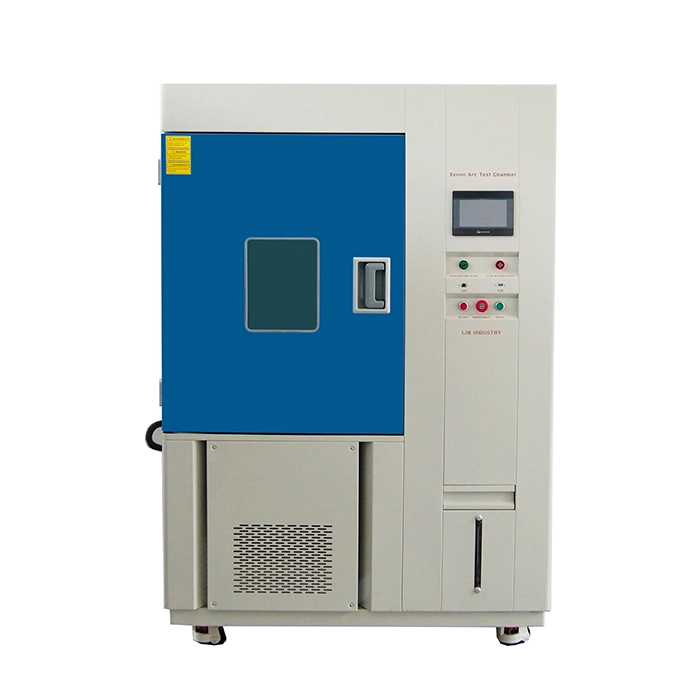
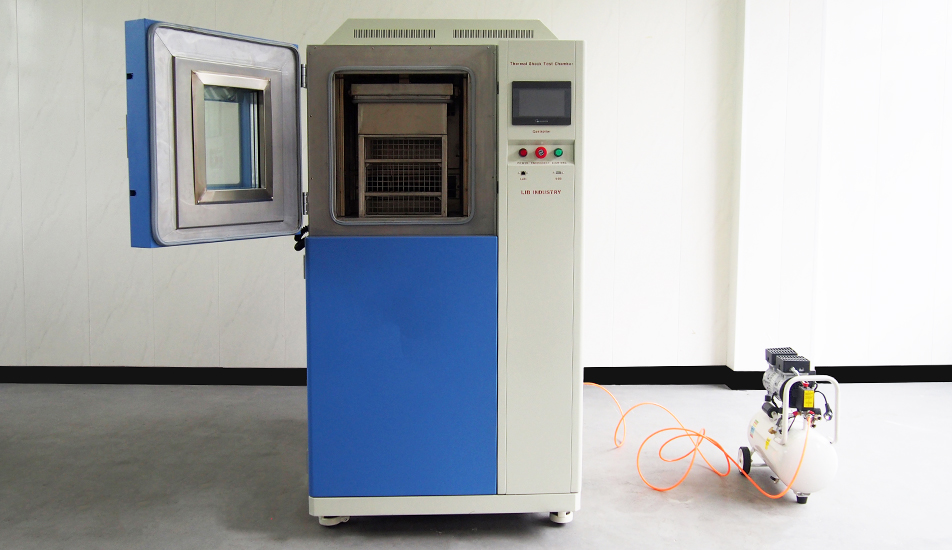
Thermal Shock Chamber Features and Benefits
1. The thermal shock chamber has upper and lower basket type and static damper type.
2. The high temperature chamber can realize air-to-air thermal shock testing, air-to-liquid and liquid-to-liquid thermal shock testing.
3. From obtaining customer needs, to discussing solutions, production, transportation, installation and commissioning, LIB can realize one-stop solutions.
4. The thermal shock environmental chambers, a kind of portable temperature humidity chamber, are mainly used in high and low temperature shock test of automobiles, EV batteries, electronic products and etc.
Specifications of Thermal Shock Chamber
Model | TS-162 | TS-340 | TS-500 | TS-1000 |
Internal Dimensions (mm) | 300*300*250 | 450*450*360 | 650*650*500 | 850*850*700 |
Overall Dimension (mm) | 1560*870*1545 | 1710*1020*1845 | 1910*1220*2265 | 2110*1420*2665 |
Interior Volume (mm) | 22L | 72L | 211L | 505L |
Loading Capacity | 20kg | 30kg | 50kg | 60kg |
Pre-heat Room | Upper limit Temperature | +220℃ |
Heating Time | Ambient ~ + 200℃, within 30 minutes |
Pre-cool Room | Lower limit Temperature | -75℃ |
Cooling time | Ambient ~ -70℃, within 30 minutes |
Test Room | High Temperature Exposure Range | Ambient +20 ~ +200°C |
Low temperature Exposure Range | –65 ~ -5°C |
Temperature Fluctuation | ≤±0.5℃ |
Temperature Deviation | ≤±3 ℃ |
Temperature Recovery Time | Within 5 minutes |
Cooling System | Mechanical compression refrigeration system |
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Ethernet connection |
Safety Device | Over-temperature protection, Over-current protection; Refrigerant high-pressure protection; Earth leakage protection |
Exterior Material | Steel Plate with protective coating |
Interior Material | SUS304 stainless steel |
Observation Window | Interior lighting, double-layer thermo stability silicone rubber sealing |
Standard Configuration | 2 shelves |
Configuration of Thermal Shock Chamber
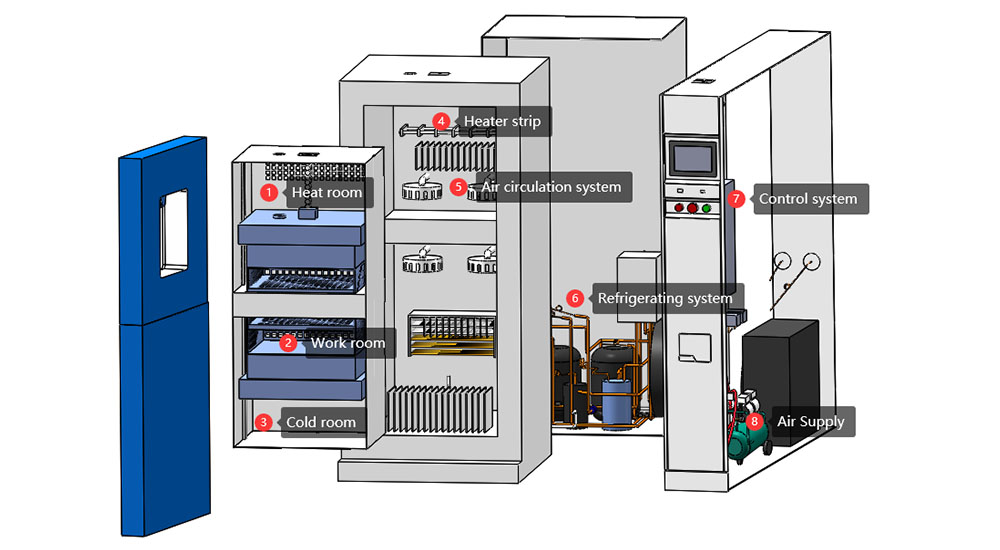
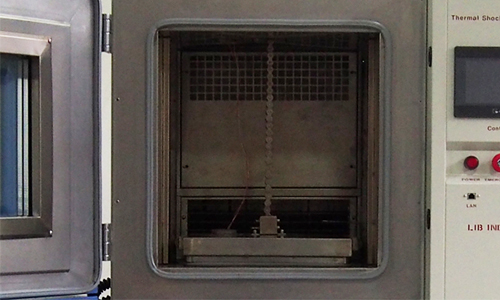
1. Heat room
| Provide a high temperature environment(upper limit temperature +220℃) and raise the temperature inside through the heater.
|  |
2. Work room | The workroom in the two-zones impact test chamber is a hanging basket, which is used to place the sample and realize the rapid switching of the sample in the high and low temperature environment (within 3 seconds). | 
|
3. Cold room | Provide a low temperature environment(lower limit temperature -75℃) and reduce the temperature inside by refrigeration devices. |  |
4. Heater strip | Nickel-chromium alloy electric heater is used to provide heat for the hot room, so that the hot chamber can reach and maintain the set high temperature. |  |
5. Air circulation system | Composed of fans,so that the air in the test chamber forms a circulation flow to ensure the uniformity of temperature. | 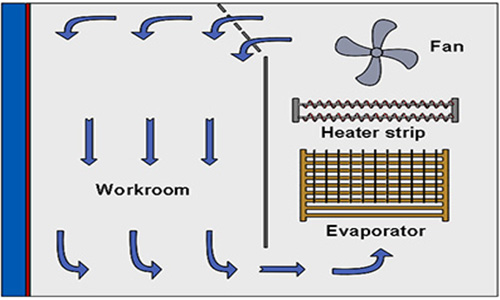 |
6. Refrigeration system | Through compressors, refrigerant circulation, etc., to achieve rapid cooling of the cold chamber and maintain the low temperature state, using R23/R404 environmentally friendly refrigerant. |  |
7. Control system | PLC controller can be set and programmed to control the temperature, time, temperature change rate and other parameters, while having monitoring, data acquisition, alarm and other functions. | 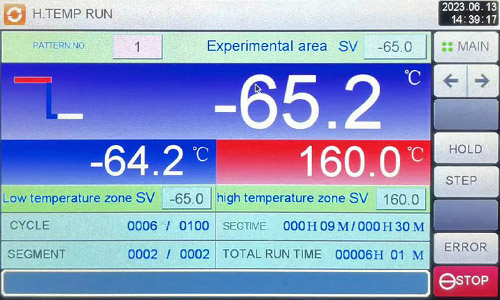 |
8. Air source | Power the pneumatic components in the equipment. |  |
A thermal shock chamber is crucial for product testing. It has two main types. The liquid to liquid thermal shock chamber immerses samples in different liquids of contrasting temperatures for rapid thermal shock. The air to air thermal shock chamber uses hot and cold airflows. Both help evaluate product reliability and durability under extreme temperature changes, ensuring product quality in various thermal environments.


 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español