It is essential that products operate stably and reliably in a variety of complex temperature environments. Thermal cycle test and thermal shock test are two commonly used temperature test methods, although they are related to temperature change, but they have their own unique properties and application scenarios, and play a key role in accurately evaluating the quality and performance of products.
Thermal cycle test to verify the effect of simulated alternating temperature changes on the mechanical and electrical properties of electronic components, test the ability of electronic components to withstand repeated temperature changes in the short term and the thermal matching performance between different structural materials, expose the potential material defects and manufacturing quality defects of components, eliminate early failures, and improve product reliability.
For example, electronic components repeatedly withstand extreme high and low temperature changes in the short term, as well as the impact of extreme temperature alternating mutations, thereby exposing the failure of components due to the mismatch of thermal expansion and contraction performance of materials, the mismatch of temperature coefficients of inner leads and tube core coatings, chip cracks, poor contact and manufacturing processes and other reasons.
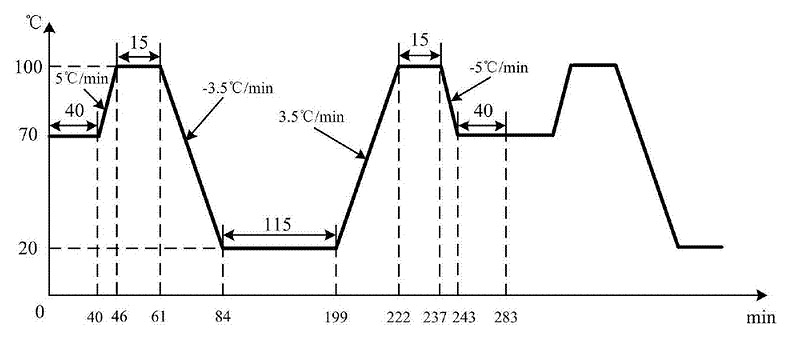
In terms of test conditions, the heating rate of the thermal cycle test is usually relatively moderate, generally in the range of several degrees to tens of degrees per minute, and the cooling process also follows a similar rate. The temperature range is set according to the ambient temperature range that the product is actually likely to encounter, for example, electronic devices may need to simulate a relatively broad but gently changing temperature band from cold winter temperatures to hot summer temperatures. A complete cycle tends to be longer, lasting hours or even days, in order to better simulate the cumulative effect of temperature on the product over a long period of use.
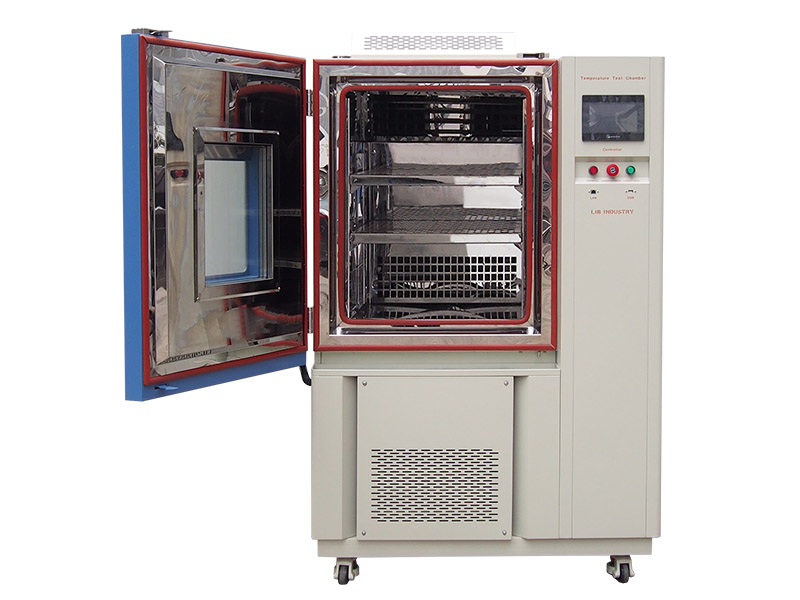

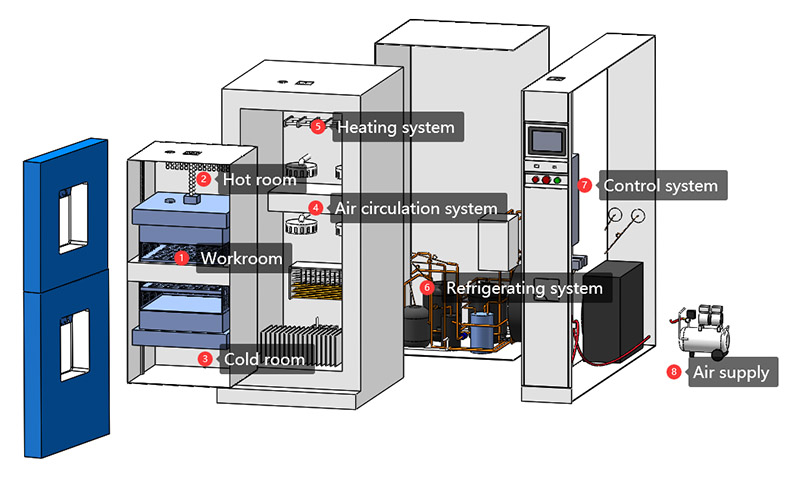
LIB thermal cycle test chamber can reach 5℃/10℃, 15℃ or higher, the use of cascade mechanical refrigeration and high-power heating wire, greatly improve the rise and cooling rate and stability, simple human-computer interaction interface, the operator can set a target temperature, the test chamber has the ability to automatically maintain constant temperature to the target temperature. LIB thermal cycle test chamber can set one or more high and low temperature changes, cycle programs, test chamber according to the preset curve to complete the test process, and can accurately control the rate of heating and cooling within the range of temperature rise and cooling rate capabilities. At the same time, through the carefully designed air duct and circulating fan, the samples in each position of the chamber can be in a stable and consistent temperature environment.
In contrast to thermal cycling tests, thermal shock tests focus on a product's ability to withstand extremely rapid temperature changes over a short period of time. The principle is to expose the product to a large temperature difference in an instant, in order to examine the product's tolerance under such extreme thermal stress.
The conditions of the thermal shock test are extremely severe. The rate of heating and cooling is extremely fast, which can reach tens of degrees per minute, and this rapid temperature change can make the product switch from a high temperature environment to a low temperature environment in an instant, or vice versa. The temperature difference of the test is usually very large, often varying dramatically between tens of degrees and hundreds of degrees, and the number of cycles is relatively small, generally only a few to dozens of cycles.
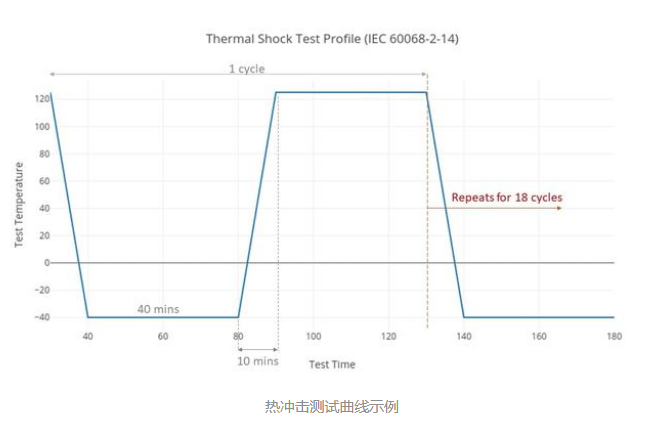
The types of thermal shock tests are more varied than thermal cycle tests:
According to the structure of the thermal shock test chamber:
with high temperature, normal temperature, low temperature three zone structure and air valve switching to achieve temperature shock, the sample remains motionless in the working room, the valve of the two cold chambers and the hot chamber is opened alternately to achieve cold and heat shock test.
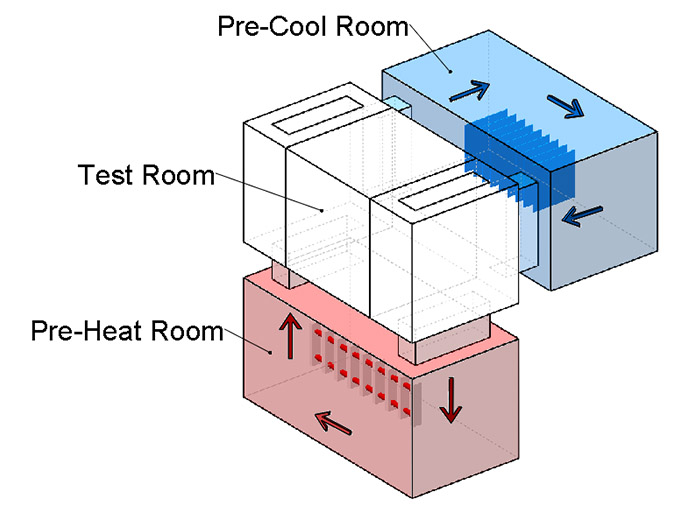
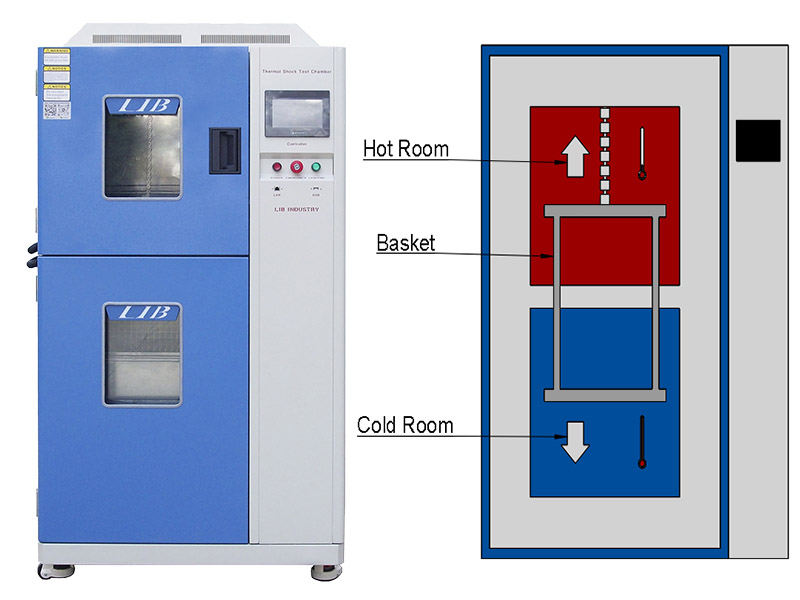
hot chamber (maximum temperature up to 220 ° C) and cold chamber (minimum temperature up to -70 ° C) and the sample in the basket rapid movement to achieve cold and thermal shock, compared with the three-chamber in terms of temperature conversion speed faster, temperature shock more harsh.
According to the temperature medium:
Using equipment such as air ducts and fans, high and low temperature air environments are formed in different areas of the test chamber. It can ensure the uniformity of temperature distribution to a certain extent, so that each part of the sample is subjected to more consistent temperature impact.
The specific heat capacity of the liquid medium is much higher than that of air. When the sample is immersed in the liquid, the liquid can quickly absorb or release a large amount of heat, achieve efficient heat transfer, and make the sample temperature change rapidly.
The sample is heated with hot air to make the surface temperature of the sample rise rapidly, and then the sample is transferred to the liquid for cooling. It can more truly simulate complex actual ambient temperature changes, and can more comprehensively evaluate the performance of products under the impact of different media temperatures, such as product sealing, thermal expansion and contraction properties of materials.
The LIB thermal shock test chamber has an independent high temperature zone and low temperature zone. Through the device that quickly changes the sample position, the sample can be transferred from the high temperature zone to the low temperature zone in a very short time, or from the low temperature zone to the high temperature zone, so as to achieve instant temperature difference impact. In order to ensure the accuracy of the test, the LIB thermal shock test chamber adopts high-performance thermal insulation materials to minimize the heat transfer interference between the high temperature and low temperature zones. At the same time, the fast response temperature control system can precisely control changes in extreme temperatures, ensuring that the conditions of each impact meet the set requirements.
From the characteristics of temperature change, the temperature change rate of thermal cycle test is gentle, the cycle period is long, and the temperature range is relatively narrow. The temperature change rate of thermal shock test is very fast, the temperature difference is large, and the number of cycles is less but more intense. This difference directly leads to the difference in the influence mechanism of the two on the product.
Under the thermal cycle test, a relatively uniform thermal stress is mainly generated inside the product. With the increase of the number of cycles, the material will gradually appear fatigue phenomenon, which is manifested as progressive performance deterioration, such as aging and deformation of the material. Due to the huge temperature difference in the moment, the thermal shock test will cause stress concentration inside the product, which is more likely to cause crack initiation, package cracking and other sudden failure modes.
In terms of test purpose and application scenario, the thermal cycle test is mainly used to evaluate the reliability and stability of the product in the conventional environment for long-term use, which is suitable for those products that work for a long time in daily life and general industrial environment. The thermal shock test is specifically used to test the tolerance of products under extreme and sudden temperature changes, which is suitable for products that may face harsh environmental mutations, such as high-end equipment in aerospace, military and some special industrial fields.
Through reasonable selection and use of these two test methods, enterprises can more comprehensively and accurately evaluate the performance of products in different temperature environments, so as to find potential quality problems and make targeted improvements. LIB has a complete product, you can thermal cycle test chamber and thermal shock test chamber, contact our team inquiry@libtestchamber.com, tell us your needs, LIB team will give you a professional solution.